SDGs+Beyond Future Society for Life Week
Investing in Sustainable District Landscapes : Scaling Indonesia's Restorative Economy
Republic of Indonesia
Indonesia is embracing a restorative economy by combining sustainable investment models with nature-based solutions, local culture, and indigenous knowledge. Districts are pioneering this shift, creating investment opportunities in agroindustry hubs, economic corridors, and nature-positive industries.
Recorded video available
Discussion
- SDGs
- post-SDGs
- future society
| Transmission of simultaneous interpretation | Provided |
|---|---|
| Language of interpretation | Japanese and English |
-
Track Programme
-
Time and
Date of
the event -
-
2025.10.03[Fri]
10:00 ~ 12:00
(Venue Open 09:30)
-
- Venue
- Pavilion
- Indonesia Pavilion
Programme details
*Subtitles: Choose “Subtitles/CC” in the “Settings” (gear
icon) at the bottom right of the YouTube video.
*Subtitles may not show with multiple languages or overlapping
audio.
The business forum highlights emerging landscapes,
regenerative land-use practices, eco-processing innovations,
and biodiversity-driven enterprises. Local governments are
fostering investment-friendly ecosystems with blended
financing and business incentives to support long-term,
scalable models. The forum connects investors, banks, and
policymakers with local leaders, offering early-mover
advantages, co-development opportunities, and access to
de-risked, sustainable business ventures. Participants will
explore ways to integrate technology and traditional wisdom,
supporting both economic growth and environmental stewardship.
Reports
【Reflection】
This programme introduced sustainable development initiatives
being implemented at the local level by the Lingkar Tem
Kabupaten Lestari (LTKL), under the support of the Indonesian
government. The session, held at the Indonesia Pavilion,
brought together a wide range of stakeholders both on-site and
online, including government officials, businesses, civil
society organisations, and young people, to discuss new models
of local economies that balance environmental conservation
with economic development.
LTKL is a network of local governments committed to improving
the welfare of local communities while protecting forests and
ecosystems by 2030. The session highlighted challenges facing
Indonesia, such as forest fires, dependence on mining, and the
ageing agricultural population, emphasising the importance of
shifting from an “extractive” economy to a “restorative”
one.
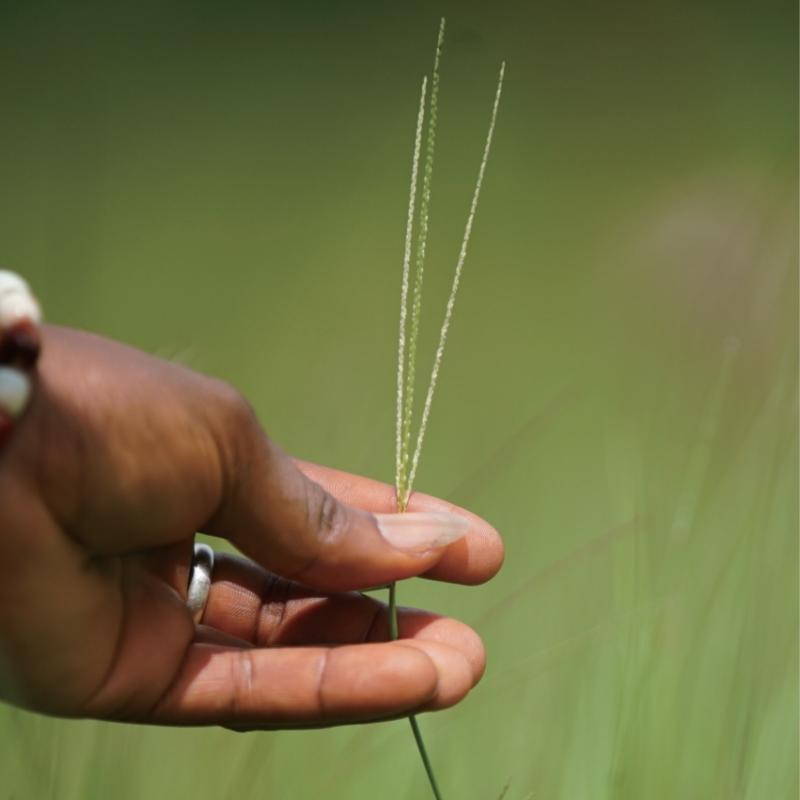
Case studies demonstrated that, even in regions prone to
natural disasters, the practice of agroforestry—combining
forestry and agriculture—contributes to both environmental
preservation and improved livelihoods. Agroforestry maintains
forests while cultivating diverse crops, conserving soil and
water resources, and providing multiple sources of income.
The session also showcased youth-led local entrepreneurship
and private sector initiatives to build agroforestry-based
supply chains, highlighting the engagement of the next
generation of talent and enterprises. These efforts have drawn
attention from participants and domestic and international
stakeholders as a means to foster self-reliant regional
economic development.
Additionally, reports on international market demand were
presented, indicating growing interest in environmentally
conscious products with high cultural value in countries
including Japan. The forum served as a practical platform for
demonstrating ways to realise a restorative economy through
the collective efforts of local communities.
【Post EXPO Initiatives】
Following the session, local governments across Indonesia have
been advancing concrete models of regional development that
balance environmental protection with economic growth.
Networks such as LTKL are expanding initiatives to build
“sustainable regency models” that leverage local natural
resources and cultural assets, with efforts already beginning
to be replicated in other regions. Moving forward,
municipalities aim to improve investment environments and
strengthen collaboration with domestic and international
businesses and financial institutions to foster long-term,
effective regional economies.
The participation of local youth and residents remains a key
factor. Initiatives such as start-up support in agriculture,
forestry, and tourism, product development using local
resources, and the promotion of eco-tourism are accelerating
across various regions. These initiatives have attracted
attention from both domestic and international stakeholders as
ways to generate new employment while preserving local culture
and the environment.
On the business side, companies are increasingly adopting
models centred on environmental restoration. A restorative
economy refers to an economic model that aims for growth while
regenerating and repairing nature, rather than merely
consuming natural resources. This approach goes beyond
conventional sustainability measures, advancing towards
enriching the natural environment itself.
Furthermore, collaboration with international markets is
expanding, with exports of sustainable materials and products
on the rise. Partnerships with overseas buyers are increasing
recognition of local brands and supporting regional economic
self-reliance. The Indonesian government views this “economy
growing with nature” as a promising new development model for
the wider Asian region.
*Part or all of this report was generated by AI.
SDGs+Beyond Future Society for Life Week
Investing in Sustainable District Landscapes : Scaling Indonesia's Restorative Economy
Indonesia is embracing a restorative economy by combining sustainable investment models with nature-based solutions, local culture, and indigenous knowledge. Districts are pioneering this shift, creating investment opportunities in agroindustry hubs, economic corridors, and nature-positive industries.
-
2025.10.03[Fri]
10:00~12:00
(Venue Open 09:30)
- Pavilion

OTHER PROGRAM
SDGs+Beyond Future Society for Life Week